What is Ponzi?
Ponzi is a type of financial fraud that has the name of Charles Ponzi, an Italian scammer who gained notoriety in the US during the early 1900s. Ponzi scammers frequently offer huge returns while utilizing the funds from new members to reimburse earlier investors. When no new players join or the leader takes all the money and runs away, this structure often referred to as a “multi-level model” will fall apart.
Ponzi schemes are a frequent type of fraud that cause significant losses in the bitcoin industry. This concept is frequently used in projects with fixed interest rates; mint tokens offer enormous rewards with minimal risk.
The first Ponzi scam was known to have occurred in the US between 1869 and 1872, and it was run by Sarah Howe and Adele Spitzeder in Germany.
The first Ponzi scam was known to have occurred in the US between 1869 and 1872, and it was run by Sarah Howe and Adele Spitzeder in Germany. These two men stole at least $40,000 a substantial sum at the time while offering female clients an 8% monthly interest rate. A similar plan was run by Charles Ponzi in 1920, but it was immediately exposed by the press; Ponzi is the term given to this technique.
How Ponzi functions?
Ponzi schemes frequently utilize ambiguous language to inflate the worth of initiatives or investment plans, such as financial investments overseas, high-profit investment programs, doing nothing but still making money, and so on, all with the promise of abnormally high interest rates. Sometimes, in order to keep information about their company model hidden, scammers will say that they employ a proprietary, top-secret investing approach. As a result, the primary victims of Ponzi schemes are investors who lack information and ability.

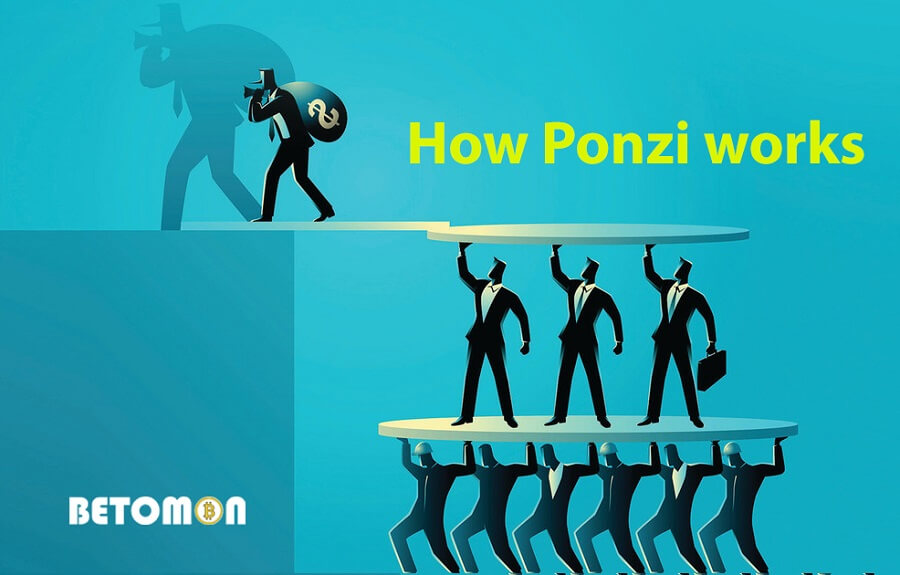
The model operates in the following specific ways:
- High yields promised: An individual or group of individuals establishes a business or investment fund with the goal of paying investors high monthly interest rates (at least 10%).
- Luring investors: The operator immediately enticed the community to participate by presenting numerous fictitious reports on investment performance and boasting of huge yields.
- Paying interest to previous investors with funds deposited by new investors: The con artist uses the money deposited by new investors to pay off previous investors instead of using it for investments. This gives the impression that the model is effective and motivates additional participation.
- System maintenance: Ponzi scheme operators must continually draw in new investors in order to pay interest to their existing clientele.
- Collapse: When too many people try to withdraw money or not enough new people sign up, the fraudster will “grab” the money and run, causing the model to fail right away. Both beginners and experienced traders lose money as a result of this.
How Ponzi works
Ponzi schemes frequently utilize ambiguous language to inflate the worth of initiatives or investment plans, such as financial investments overseas, high-profit investment programs, doing nothing but still making money, and so on, all with the promise of abnormally high interest rates. Sometimes, Fraudsters will say they protect details about their business model by using a proprietary, top-secret investing technique. As a result, Ponzi schemes mostly target investors who lack expertise and resources.
The model operates in the following specific ways:
- High yields promised: An individual or group of individuals establishes a business or investment fund with the goal of paying investors high monthly interest rates (at least 10%).
- Luring investors: The operator immediately enticed the community to participate by presenting numerous fictitious reports on investment performance and boasting of huge yields.
- Paying interest to old investors with funds deposited by new investors: The con artist does not invest the money that new investors deposit; instead, interest is paid to them. This makes it seem as though the model is functioning effectively and motivates additional participation.
- Maintaining the system: Ponzi operators must continually draw in new investors in order to reimburse previous investors for their interest.
- Collapse: The fraudster will “grab” the money and run away, causing the model to collapse right away when there aren’t enough new members or when there are too many people attempting to withdraw money. This results in asset losses for both inexperienced and experienced traders.
Signs of Ponzi
The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) claims that Ponzi has several notable qualities. Investors can then identify, choose not to engage, and alert other people.
- High profits, no risk: All investments, particularly those in the cryptocurrency space, have some risk, which varies according to the potential return. Platforms that guarantee substantial earnings with little to no risk could therefore be scam initiatives.
- Profits are too stable: Real-time fluctuations are a constant in the investing process, particularly with values that have a large potential for profit, like tokens or NFTs. A project that consistently turns a profit in spite of market trends and changes is seen as a scam.
- Unlicensed financial institutions and investment funds: Investors should be cautious when dealing with investments that are not registered with national commissions or finance ministries. This lessens the number of Ponzi schemes by enabling investors to obtain financial management data, financial institution goods, and services.

Because cryptocurrency initiatives are decentralized, secure, unrecognized, and popular in many countries, it is common to find the symptoms listed above in many of them. Investors in digital assets are frequently swayed by the FOMO phenomenon and lack sufficient understanding prior to investing, making them susceptible to falling prey to Ponzi schemes.
Some Ponzi projects in the crypto market
FTX
One of the most obvious examples of Ponzi schemes is FTX’s collapse. In 2022, the platform held the second-largest volume globally and was the most popular exchange. Through the ICO program, the project raised $4.56 million by issuing FTT tokens. The platform call that was successful has a total investment capital of $1.75 billion.
CoinDesk revealed in November 2022 that Alameda Research, a significant project partner, had misused user assets. Many become doubtful about FTX’s safety and openness as a result.

Sam Bankman-Fried, the originator of the site, was promptly the subject of an investigation by the US court over seven charges. As to the SEC, FTX misappropriated funds belonging to investors and users and utilized millions of dollars for marketing activities aimed at drawing in new consumers. Sam Bankman-Fried was found guilty on March 28 and sentenced to 25 years in jail in addition to paying $11.2 billion in fines.
OneCoin
OneCoin first presented itself as a distinct cryptocurrency company, hoping to set itself apart from Bitcoin in terms of technology. The project offers technological training as part of its business plan and offers awards to users who successfully bring new members to the site, up to 5% of total revenue.

With over 3.5 million users, OneCoin made $4.3 billion between its establishment in 2014 and 2016. But at the close of 2016, a large number of investors pulled their money out of the enterprise due to concerns about its actual business plan. The US Department of Justice was inspired and encouraged to look into the platform by this wave.
OneCoin was accused of running a Ponzi scam in October 2017 and was prohibited from publishing any courses or products that might be considered plagiarized. The project’s creator quickly left with all of the investors’ money.
BitConnect
Launched in November 2016, BitConnect is a scam project built on the Ponzi model. With the launch of its ICO campaign and BCC coin issue, the platform immediately caught the interest of investors. For $1.84, BitConnect sold more than one million tokens.
The BCC token increased more than 50 times and a trade of $59.24 in June 2017. Due to the FOMO phenomenon, traders start making large purchases as a result. In January 2018, the Texas Securities Commission (USA) shut down BitConnect on the grounds that company was engaging in Ponzi schemes.

The project’s official website announced maintenance, restricted users’ ability to withdraw, and officially ended operations on January 16, 2018, immediately following the claims. For thousands of investors, the incident resulted in losses of almost $2 billion.
>>> What is FOMO? The FOMO effect during an uptrend market
Conclusion
Ponzi or multi-level fraud is a prevalent form that causes losses in numerous industries, including the cryptocurrency sector. Ponzi merely requires investments as opposed to the multi-level pyramid model’s requirement to buy products, making it simpler to steal participants’ assets. To prevent losing their digital assets, investors should think things through thoroughly before investing in initiatives and financial organizations.
Betomon is a website that reviews, analyzes and knowledge shares about safe and stable financial investment projects on the theme of crypto forex blockchain… Projects to make money online for free
Visit the website betomon.com or register to receive the latest information here.




